
Disasters are unpredictable, but a solid business continuity plan ensures your company can recover quickly. Whether it’s cyberattacks, system failures, or natural calamities, you need a robust Disaster Recovery strategy that defines clear recovery objectives. The two core metrics are Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO), which help protect critical data and ensure smooth business operations. In this article, we’ll explain these concepts and how they strengthen IT resilience, especially in Cloud and data center environments.
What Is Disaster Recovery?
Disaster Recovery is the discipline that enables an organization to recover its IT systems, data, and operations smoothly and efficiently after being affected by a disruptive event. A successful Disaster Recovery (DR) plan minimizes downtime, mitigates data loss, and ensures business continuity, all essential for protecting revenue, maintaining trust, and ensuring compliance. It also defines how you protect critical data and choose the right recovery solutions to restore systems and operations.

What Is RPO?
Recovery Point Objective (RPO) defines the maximum amount of data loss that is acceptable, measured in time. In simple terms, it answers the question:
“How much data can we afford to lose if systems go down?”
- For mission-critical apps, your RPO might be in minutes.
- For non-essential systems, it might be hours
Example: If your RPO is 15 minutes, your backup systems must capture data at least every 15 minutes.
What Is RTO?
Recovery Time Objective (RTO) refers to the maximum allowable downtime after an incident before your systems must be back online. It answers:
“How quickly do we need to recover to avoid a significant impact?”
- RTO helps you define SLAs, backup frequency, and system architecture.
- Business needs, compliance requirements, and cost often determine it.
Example: If your RTO is 2 hours, your DR solution must fully restore functionality within that window.
Your recovery process must align with your Recovery Time Objective (RTO) to ensure minimal downtime for essential business operations.
Why RPO and RTO Matter in Disaster Recovery
Without a defined RPO and RTO, you risk:
- Prolonged downtime
- Irreversible data loss
- Lost revenue & reputation damage
- Non-compliance with regulatory requirements
Clear recovery objectives help maintain data protection and align your disaster recovery strategy with overall business goals.
According to IBM, the average cost of a data breach in 2023 was $4.45 million, underscoring the importance of robust disaster recovery (DR) strategies.
Key Components of a Disaster Recovery Plan
A strong DR plan includes:
- Risk Assessment & Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
- Defined RPO & RTO metrics
- Data Backup & Replication
- Data Recovery Procedures
- Defined Recovery Solutions
- Cloud& On-Prem Infrastructure Integration
- Automated Failover Systems
- Recovery Testing & Drills
- Clear Documentation & Communication Plan
Best Practices for Implementing RPO and RTO
- Set realistic RPO/RTO goals based on application priority
- Leverage cloud-native DR tools for agility and automation
- Automate Backups using tools like Wanclouds VPC+
- Test Disaster Recovery plans regularly
- Document recovery procedures clearly
- Ensure compliance and data security
Regular testing validates your data recovery capabilities and strengthens your disaster recovery strategy.
Common Challenges in Disaster Recovery
- Budget and resource constraints
- Inconsistent backup schedules
- Compatibility issues during failover
- Data corruption or ransomware attacks
- Difficulty maintaining DR plans across Multi-Cloud environments
Solution: Platforms like Wanclouds VPC+ Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) provide full-stack automation, cross-Cloud mobility, and ransomware detection.
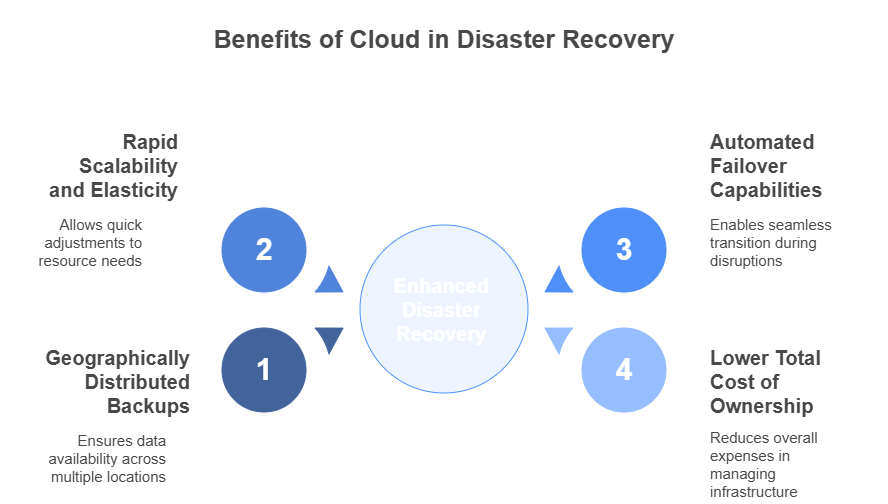
Role of Cloud in Disaster Recovery
Cloud has transformed DR by offering:
- Geographically distributed backups
- Rapid scalability and elasticity
- Automated failover capabilities
- Lower total cost of ownership (TCO)
- Improved data protection and critical data recovery
With Wanclouds VPC+, you can:
- Create custom Backup schedules
- Automate Multi-Cloud Migration & restoration
- Detect and respond to ransomware events
- Manage all workloads from a single dashboard
Conclusion
Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO) are the backbone of any business continuity plan and disaster recovery strategy. They guide your strategy, influence technology decisions, and determine your readiness for the unexpected.
With tools like Wanclouds VPC+ DRaaS, you can automate backup, recovery, and resilience in complex Cloud and hybrid environments, reducing risk, cost, and downtime.
Need help calculating your ideal RPO and RTO? Contact Wanclouds today for a complimentary Disaster Recovery (DR) assessment. NIST Contingency Planning Guide – a U.S. federal standard defining RPO and RTO for IT continuity planning.